Material properties
Combar® has special characteristics which give the glass fibre composite material a decisive advantage over conventional steel reinforcement in certain areas.



Only certified components are used when manufacturing Schöck Combar®. Both glass and also resin, hardeners and other components must satisfy the most stringent quality standards. Only a precisely defined particularly corrosion-resistant ECR (“E-Glass Corrosion Resistant”) glass fibre type is approved for use in Schöck Combar®. Owing to these special components, a resistance of 100 years can be achieved in highly alkaline concrete and at higher temperatures.
Schöck Combar® is electrically non-conductive which means that induction does not occur in the bar in the presence of a variable magnetic field. This eliminates heating of the reinforcement and stray current corrosion which would otherwise occur as a result of induction. This also avoids malfunctions of signalling and control systems.
Schöck Combar® is non-magnetisable. Highly sensitive measuring instruments are therefore not exposed to magnetic interference.
Schöck Combar® is made of glass fibres arranged in parallel fibre bundles by skilfully guiding them and applying tension. In the longitudinal direction of the fibres, Schöck Combar® has high strength. However, when exposed to lateral pressure the fibres are only capable of absorbing much lower forces. The machinability is therefore good. This characteristic gives it a decisive advantage over reinforcing steel in the field of tunnelling. Schöck Combar® makes light work of excavation by the tunnel boring machine in the shaft area.
| char. value of tensile strength ftk (N/mm²) | 550 | 550 | > 1000 | |
| char. value of strain limit fyk (N/mm²) | 500 | 500 | no flow | |
| Design value of strain limit fyd (N/mm²) | 435 | 435 | 445 | |
| Elongation at ultimate limit state of load-bearing capacity | 2,18 ‰ | 2,72 ‰ | 7,4 ‰ | |
| Bending value Young's modulus (N/mm²) | 200.000 | 160.000 | 60.000 | |
| Design value of transfer bond fbd | C20/25 (N/ mm²) | 2,3 | 2,3 | 2,03 |
| C30/37 (N/mm²) | 3,0 | 3,0 | 2,33 | |
| Min. concrete cover cv | according to EC 2 | ds + 10 mm | ds + 10 mm | |
| Density γ (g/cm³) | 7,85 | 7,85 | 2,2 | |
| Thermal conductivity λ (W/mK) | 60 | 15 | 0.7 | |
| Linear coefficient of therm. expansion α (1/K) | 0.8 - 1.2 · 10-5 | 1.2 - 1.6 · 10-5 | 0.6x10-5 | |
| Magnetism | yes | very low | no | |
| Characteristic* | Reinforcing steel B500 A/B | ribbed stainless steel B500 NR | Schöck Combar® | |
*All designations according to EC 2
In contrast to steel, Schöck Combar® behaves in a linear elastic manner until failure. The measured Young's modulus is higher than 60,000 N/mm² in contrast to reinforcing steel with 200,000 N/mm². The characteristic tensile strength of the glass fibre composite material Combar® is higher than 1000 N/mm².
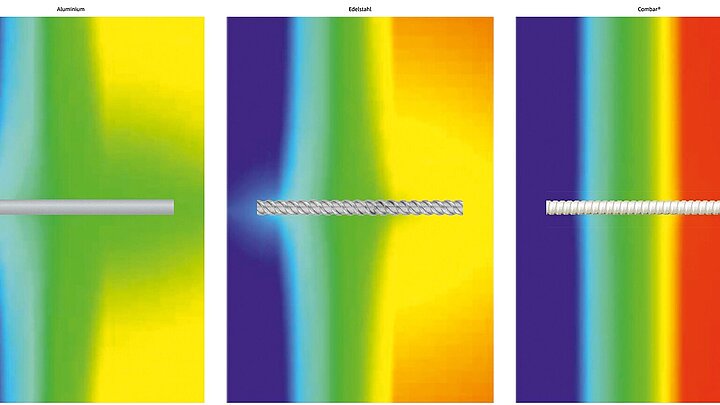
Schöck Combar® has an exceptionally low thermal conductivity and is suitable for installation in the insulating layer. Tension bars made of glass fibre composite material are therefore used in the Schöck Isokorb® CXT. The improved thermal insulation performance makes additional cantilevers possible in Passive Houses and low energy homes with the same heat emission. The Schöck Isolink® façade anchor is made of fibre-composite material and minimises thermal bridges in the façade.

